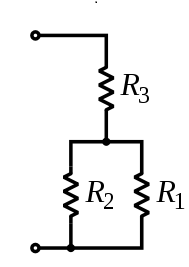
A resistor is a passive electronics component that uses to provide electrical resistances on a circuit. Its main functions are to reduce the current flow on serial and reduce the voltage when it is connected parallel. Mainly two types are named fixed resistances and variable resistances. Here the fixed resistance named simply resistor and the variable resistances are named thermistors, varistors, trimmers,photoresistors and potentiometers.
 The current through the circuit can be calculated by Ohm's law, that is, I= V/R.
The current through the circuit can be calculated by Ohm's law, that is, I= V/R.
Where I is the current flows through the resistor in amperes, V is the potential difference across the resistor in volts and R is the resistance provided by the resistor in ohms.
 The current through the circuit can be calculated by Ohm's law, that is, I= V/R.
The current through the circuit can be calculated by Ohm's law, that is, I= V/R.Where I is the current flows through the resistor in amperes, V is the potential difference across the resistor in volts and R is the resistance provided by the resistor in ohms.